Issues Detected, But What Are They?
I would suggest that because you have checked the cable between the monitor and the pc you have confirmed that the monitor is okay because you are getting the message that it is receiving no signal. I would unplug everything that you can including the power cord from any and all ends one at a time and plug them in again because I think your next move after checking for obvious damage is to take it to a technician. I am afraid it sounds like something is broken in the pc. May not be a big repair but may be it is. Hope it is just a broken wire. The problem is could be damage to your video card; perhaps when the tower fell it damaged whichever receptacle on the back of your computer you have your monitor plugged into. Usually there are several, with most recent cards having at least a VGA and a DVI.
If you just bought a new monitor you probably have the necessary cables to try using the OTHER one. The impact of the fall may have caused the connection between your video card and your motherboard to come loose, or (and this is HIGHLY unlikely) caused the plug from the power supply to your video card to dislodge - it would be the only wire running to the video card. Unplug everything, open your case, unplug the power connection to your video card, remove and reseat your video card and plug it back into the power supply. If it still doesn't work you may need to replace the video card. If THAT doesn't work, try it in another slot (most motherboards have more than one PCI slot, which is probably what your video card uses). If THAT doesn't work you may need a new motherboard, and it might be a simpler matter just to get a new PC.
Notes:. If you have more than one webcam, all should appear in the drop-down list. If the camera doesn't appear in the list.
Is your camera plugged in? If you’re using an external instead of a built-in webcam, make sure that it’s plugged in and turned on. If it’s connected to your computer by USB, try plugging it into a different USB slot. If you’re using a USB hub, try plugging the camera directly into a USB slot on your computer instead—and try disconnecting other USB devices. Is your webcam installed correctly? Check that your camera is listed and enabled in Device Manager, even if you’re using the computer’s built-in camera. To open the Device Manager.
In Windows 10 and Windows 8 desktop, tap the Windows logo key ( Start) and type Device Manager in the search box. If necessary, choose the administrative tool from the results. In Windows 7, choose the Windows logo key ( Start) Control Panel. In the View by browse control items, choose Category. Choose Hardware and Sound, and then under Devices and Printers, choose Device Manager. Under Imaging devices, check that your camera is listed.
If it's listed, make sure it’s enabled. If you see a Disable option, then the camera is enabled. If you don't, right-click and choose Enable. If it isn't listed, or if there's a question mark or exclamation mark, you’ll need to reinstall the camera.
You can find the latest drivers for your camera on the Internet. Searching for the camera model on. If the camera shows up in the list but doesn't show preview. Is another application using your webcam? Close any applications that might be using your webcam, including video editing software, virtual camera software, instant messengers and Internet browsers.
If your webcam has a light to show when it’s in use and you see it when you’re not in a call, then some other application is using your camera. Check camera privacy settings. Some cameras have 'Privacy' setting.
Choose Camera Settings and disable the setting. If you only see a solid black frame in video preview, your camera might have a physical privacy shutter. Open the shutter to enable the video. If video quality is poor—meaning that call participants can see each other’s video feed but the picture is too dark, blurred, or pixelated, or the picture freezes—the following tips might can help:. Check your connection If the video freezes, looks block-like, or has motion blur, it might be your Internet connection (or another participant’s Internet connection) causing the problem. If Skype for Business detects a weak connection, it'll reduce the quality to try and stop the call from dropping altogether.
Review our guide to. Improve the lighting conditions A well-lighted room can make a big difference with the video quality of your calls. If the room is too dark, your webcam will try to amplify the signal to make the picture brighter, which reduces the video quality. Also if you have a window(s) or a bright light source behind you, for example, your face will appear dark and featureless to the other participant. For best results, make sure there's enough ambient light, and avoid back light.
Check your camera settings In the Skype for Business main window, go to Tools Video Device settings. You’ll see what your camera sees in the window. Choose Camera Settings to access the settings of the used webcam. We recommend using the default settings to let the camera automatically adapt to the lighting conditions. It might be necessary, however, to manually change some settings. For example, the anti-flicker setting might not be set correctly for the 50 Hz (hertz) or 60 Hz wall power setting in your area.
Upgrade your camera Built-in cameras in older laptops and tablets might not produce the best results. You might want to invest in a newer webcam. Most external webcams work with Skype for Business, but the best experience is guaranteed by using a Skype for Business Certified webcam listed in the. If you’re already using an external camera and you’re having problems with video, try plugging it into a different USB port.
If other participants can't hear anything from your side, the problem is either with your microphone or with their playback device (speakers or headphones). Check your settings in Skype for Business. Skype for Business automatically mutes people joining a scheduled conference.
This is done to reduce the noise from parties that aren't active presenters. To unmute yourself, choose the microphone icon with the diagonal line in the call window. Check your microphone. If you’re using your computer’s built-in microphone, make sure it isn't muted. If you’re using an external microphone, check that its plugged in.
If it’s a wireless microphone, make sure the batteries are charged. Also check for physical mute buttons on the headset/headset cord. Make sure that the correct device is selected.
Watch this for detailed instructions about checking your audio and video settings. Or, follow the steps below. On the lower-left side of the Skype for Business main window, choose Audio Device Settings. If you want to use different devices for audio input and output, then choose Custom Device. This opens separate drop-down lists for Speaker and Microphone.
In the Microphone drop-down list, choose the mic you want to use. If you only use your computer’s built-in microphone, you’ll see just one option. Speak into the microphone. If the microphone can hear you, the blue speech activity indicator bar will move up and down (the farther right it reaches the better the signal level is). If you have more than one microphone and you’re not sure which name relates to which microphone, talk into each microphone in turn and check the blue speech activity indicator for movement. Make a test call. On the lower-left side of the Skype for Business main window, choose Check Call Quality.
Note: This feature isn't available yet for Skype for Business Online users. If you can hear your recorded message played back, then your microphone is working fine. The problem might be with another participant’s connection or playback device. Suggest the participant review this guide to solve speaker or headset issues. If you can’t hear your recorded message, continue through these steps to check your Windows audio settings.
Check your Windows settings. Adjust the signal strength (boost) of the microphone in Windows by right-clicking the loudspeaker icon at the bottom-right of the screen and using the slider control. Choose Recording devices. Right-click the device Skype for Business uses and choose Properties.
Then, on the Levels tab, use the slider control to adjust the volume. If these steps haven’t helped resolve the issue, you might have a problem with your Windows audio settings. Microsoft has a tool to. If the audio quality is poor—meaning that the other participant can hear you but your voice echoes, sounds muffled, or drops in and out—the following tips can help.
Check your connection. If there are gaps or delays in the audio or if a participant starts sounding like a robot, it might be your or another participant's Internet connection causing the problem. See in this guide.
Make sure that the correct device is selected. On the lower-left side of the Skype for Business main window and choose a device from Select Primary Device.
Check your Audio Device Settings. On the lower-left side of the Skype for Business main window, choose Audio Device Settings.
Adjust the volume control under selected Microphone and check that, when speaking normally, at least one-third of the sound detected fills the box. If the level indicator can't reach it, then try to increase the signal strength of the microphone in Windows by right-clicking the loudspeaker icon at the bottom-right of the screen. Select Recording devices. Right-click the device Skype for Business uses and choose Properties. On the Levels tab, use the slider control to increase (boost) the strength of microphone's signal if that setting is available.
Improve the speech to noise ratio. The best way to improve audio quality is by increasing the contrast between the sound of your voice and all other sounds around you. There are lots of ways to do this. In case of speakerphone or webcam move closer to the microphone. Being too far away from your microphone makes it hard for the mic to pick up your voice clearly. If you’re using the built-in microphone on your computer, make sure you know where it is and make sure nothing is blocking it.
For tablet devices, make sure your hand or a finger is not blocking the microphone entrance when you hold the device. Reduce background noise. Quiet spaces are best for audio quality because there is less ambient noise for your voice to compete with. Built-in microphones tend to pick up sound from all around. Reduce the volume of the playback.
If the volume of your speakers is too loud, or if the speakers are too close to your microphone, either condition can cause interference or echo. Turn down the volume on your speakers and, if possible, move them farther away from the microphone. Use a headset. Almost all the issues described can be improved or solved by using a USB headset.
All USB headsets work with Skype for Business, but the best experience is guaranteed by using a Skype for Business Certified headset listed in the. If the headset is new and you’re having problems with audio, try plugging it into a different USB port. Also check for hardware level microphone mute. On some headsets, for example, rotating the microphone boom up toward the ceiling equals “mute.” Consult the headset quick start guide or user guide for information about the proper operation of the headset.
Solve speaker or headphone issues If you can’t hear the other participant at all, or can’t hear them very well, there might be something wrong with your playback device (speakers or headphones) or settings. If you can’t hear anything from the other participants, the problem is either with one of their microphones, or with your playback device. Make sure the correct device is selected.
Watch this for the detailed instructions about how to check your audio and video settings, or follow the steps below. On the lower-left side of the Skype for Business main window, choose Audio Device Settings. If you want to use different devices for audio input and output, choose Custom Device. This selection opens separate drop-down menus for Speaker and Microphone. In the Speakers drop-down list, choose t the playback device you want to use.
Issues Detected But What Are They Called
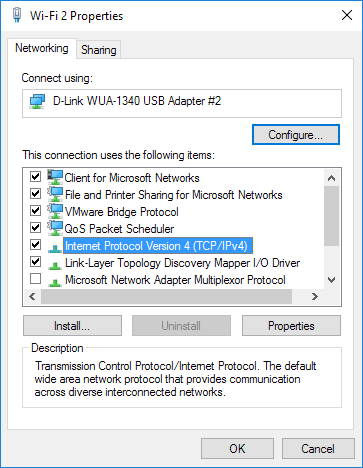
If you only have your computer’s built-in speakers, you’ll see one option in the drop-down list. If you’re using headphones or external speakers, make sure you choose the correct option. Choose the play icon to test your speakers. Make a test call. Note: This feature is not yet available for Skype for Business Online users.
On the lower-left side of the Skype for Business main window, choose Check Call Quality. If you can hear the voice on the test call, then your audio is working fine. The problem might be with a participant's connection or microphone.
If you can, ask the participant whom you can’t hear to review this guide to solve microphone issues. If you can’t hear the voice on the test call, continue with these steps to check your audio settings in Skype for Business. Check your Windows settings. Make sure the speaker volume isn’t muted and is high enough for you to hear it.
Choose the loudspeaker icon at the bottom-right of the screen to adjust the volume. The volume slider control is for the system default playback device. If you have multiple playback devices, Skype for Business might be using a different one. To change the volume for other devices, right-click the loudspeaker icon and choose Playback devices. Right-click the device Skype for Business uses and choose Properties.
Then on the Levels tab, use the slider control to adjust the volume. If these steps haven’t helped, you might have a problem with your Windows audio settings. Microsoft has a tool to. If the audio quality is poor—meaning that you can hear the other participant but their voice sounds muffled, or echoes, or drops in and out—the following tips can help.
Check your playback device. If the other participant sounds quiet, you might need to turn up your speaker volume. Choose the loudspeaker icon at the bottom-right of the screen to adjust the volume. The volume slider control is for the system default playback device. If you have multiple playback devices, Skype for Business might be using a different one.
To change the volume for other devices, right-click the loudspeaker icon (shown above) and choose Playback devices. Right-click the device Skype uses, choose Properties, and then on the Levels tab, use the slider control to adjust the volume. Check in-client volume control. On the lower-left side of the Skype for Business main window, click Audio Device Settings. Move the Speaker slider control and choose the play icon to test your speakers. Alternatively, during a call it is accessible from the call window by choosing the Call Controls button. Check your connection.
If there are gaps or delays in the audio, it might be your Internet connection (or the other participant’s) causing the problem. See in this guide. Improve the sound at the other end.
If you hear background noise in a conference call. Choose the Participants button, and then look at the microphone icon for each participant. The icons indicate activity and if the background noise matches with a non-presenter then you should ask that participant to mute their microphone. If you're a presenter, you can mute the participant yourself. Ask the other participant to follow the tips in this guide to solve microphone issues.
Issues Detected But What Are They Among So Many
There are many ways to improve the speech-to-noise ratio, which will make it easier for you to more clearly hear the participant. Having connection problems with your Skype for Business calls?
